Disorders
- Anorexia Nervosa
- Binge Eating Disorder
- Bitot's Spots
- Bulimia Nervosa
- Macrocytic Anemia
- Megaloblastic Anemia
- Night Blindness
- Peptic Ulcer
- Prophylaxis
- Rhodopsin
- Rickets Disease
- Scurvy Disease
- Wilson’s Disease
- Xerophthalmia
- Hemochromatosis
- Siderosis
- Thalassemia
- Sideroblastic Anemia
- Porphyria Cutanea Tarda
- Sickle Cell Anemia
- Kwashiorkor
- Menkes Disease
- Neutropenia
- Keratomalacia
- Beriberi
- Pellagra
- Macrocytic
- Megaloblastic
- Pernicious Anemia
- Scurvy
- Rickets
- Osteomalacia
- Abetalipoproteinemia
- Muscular Dystrophy
- Haemolytic Anaemia
- Cholestatic Constipation
- Pretibial Myxedema
- Cretinism Diesease
- Hypothyroidism
- Hypothyroidism
- Feline Hyperthyroidism
- Graves Disease
- Plummer’s Disease
- Thyrotoxicosis
- Acrodermatitis Enteropathica
- Congenital Hypothyroidism
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
- Hyperthyroidism
- Keshan Disease
- Lose Weight with Hypothyroidism
- Metal Fume Fever
- Postpartum Thyroiditis
- Thyroid Storm
- Subclinical Hypothyroidism
Prophylaxis
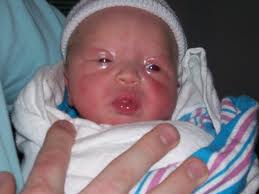
When it comes to talking about eye prophylaxis, one is referring to eye drops or ointment containing an antibiotic medication that is placed in a newborn's eyes after birth. This is a widely spread protection method required by law to protect the baby from serious eye infections in the mother's body. Newborns are at risk by exposure in the birth canal to conjunctivitis, gonorrhea or chlamydia, which may be asymptomatic in the mother.
The use of antibiotics to practice eye prophylaxis is required in most hospitals, the same as another preparation such as silver nitrate, tetracycline or erythromycin. In any case, the ointment or drops may cause a baby's eyes to appear cloudy and the eyes of few newborns may become very irritated with redness or swelling as a temporary condition while the medication should not be washed or cleaned out of the eyes.
Neonatal ocular prophylaxis is not necessary according to medical studies that prove the eye ointment applied to newborns does not alter eye infections at all as opposed to no ointment of any kind. However, they say there is evidence that the bacteria which cause such infections are not passed by the mother to the infant in the birth canal, but after birth when it is not necessary but mandatory.
Back in the 1950s, X rays were used commonly with baby’s then, by the 1970s the silver nitrate was routinely used as an eye prophylaxis for newborn babies although many mothers refused it because it blurred the newborn's eyes during the sensitive bonding period. At the present, health care professionals prefer antibiotics such as erythromycin, which is the eye prophylaxis of choice.
Another fact found during the study of neonatal eye prophylaxis found that a significant number of infants tend to develop an infection despite the fact they received one of the fore mentioned ointments . Those studies seems to suggest that parental choice of a prophylaxis agent, or no prophylaxis, is reasonable for women receiving prenatal care or have been screened for sexually transmitted diseases during pregnancy.
Instead of antibiotics, another eye prophylaxis method suggests the use of vitamin K injections. This vitamin is an essential component of blood clotting that under normal circumstances is produced by intestinal bacteria. It is normal that babies have low levels of this vitamin and nutrients in their bodies so, in order to prevent a serious bleeding problem, most babies receive an injection of vitamin K in the upper thigh. This may be momentarily painful to the baby, but it does not seem to cause babies any pain afterwards and protects him efficiently from such bleeding called Hemorrhagic Disease of the Newborn (HDN).
Babies will experience many important medical procedures in the early days of their lives, many of them mandated by law, including apgar evaluation, eye prophylaxis, vitamin K injection, newborn metabolic screening, blood sugar testing and hepatitis B vaccine.
Because the eye treatment can sting or blur the baby's vision temporarily, this is a procedure you especially may wish to postpone until you have fed and bonded with your baby. The state and federal guidelines remark the importance that all newborns receive vitamin K and eye prophylaxis within the first hour after birth was a barrier to effective breastfeeding. Then the newborns are separated from the mother to receive attention in the nursery with a health care professional administered vitamin K and eye prophylaxis in the labor and delivery room.
Sometimes, newborns are exposed to chemical conjunctivitis that usually occurs within 24 hours of instillation of eye prophylaxis after birth, presenting mild lid edema with sterile discharge from eyes, but this condition usually resolves by itself within 48 hours after birth.
