Disorders
- Anorexia Nervosa
- Binge Eating Disorder
- Bitot's Spots
- Bulimia Nervosa
- Macrocytic Anemia
- Megaloblastic Anemia
- Night Blindness
- Peptic Ulcer
- Prophylaxis
- Rhodopsin
- Rickets Disease
- Scurvy Disease
- Wilson’s Disease
- Xerophthalmia
- Hemochromatosis
- Siderosis
- Thalassemia
- Sideroblastic Anemia
- Porphyria Cutanea Tarda
- Sickle Cell Anemia
- Kwashiorkor
- Menkes Disease
- Neutropenia
- Keratomalacia
- Beriberi
- Pellagra
- Macrocytic
- Megaloblastic
- Pernicious Anemia
- Scurvy
- Rickets
- Osteomalacia
- Abetalipoproteinemia
- Muscular Dystrophy
- Haemolytic Anaemia
- Cholestatic Constipation
- Pretibial Myxedema
- Cretinism Diesease
- Hypothyroidism
- Hypothyroidism
- Feline Hyperthyroidism
- Graves Disease
- Plummer’s Disease
- Thyrotoxicosis
- Acrodermatitis Enteropathica
- Congenital Hypothyroidism
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
- Hyperthyroidism
- Keshan Disease
- Lose Weight with Hypothyroidism
- Metal Fume Fever
- Postpartum Thyroiditis
- Thyroid Storm
- Subclinical Hypothyroidism
Hyperthyroidism: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
What is Hyperthyroidism?
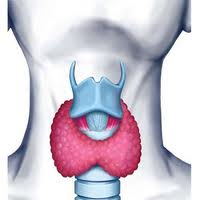
Hyperthyroidism affects every part of the body especially when it’s out of balances and not functioning properly. Normal thyroid function produces two types of hormones T4 and T3 which control your metabolism and turns oxygen into calories to burn energy resulting in lose of weight or a maintained weight balance. Your pituitary glad produces a thyroid stimulating hormone which raises the level TSH level resulting in hyperthyroidism.
What are the signs and symptoms of Hyperthyroidism?
The most common signs and symptoms of Hyperthyroidism are heart palpitations, heat intolerance, insomnia, nervousness, anxiety, irritability, shortness of breath, fatigue, light or absent menses, increase in bowel movements, hand tremors, weight loss, muscle weakness, loss of hair, clammy skin, memory loss.
What parts of your body does Hyperthyroidism effect?
What causes Hyperthyroidism?
One of the most common causes of hyperthyroidism is Graves disease which is an autoimmune disease caused by your immune system attacking your thyroid gland. Causing swelling around the eye’s called facial edema, swelling and thickening of the skin on the legs and feet, and obviously an over active thyroid. Some patients experience inflammation around the eyes which causes the eyes to bulge and irritated eye’s causing blurry vision, double vision. If these conditions go untreated the symptoms can damage your eye’s permanent damage even worse causing blindness. Less common causes of hyperthyroidism are nodules which are non cancerous lumps or tumors inside your thyroid gland which can produce massive amounts of thyroid hormones causing hyperthyroidism. Inflammation of the thyroid gland can release excess amounts of thyroid hormone resulting in a painful inflamed glad which is called thyroiditis resulting in hyperthyroidism, Postpartum thyroiditis which effect women after child birth which generally lasts short period of time before your hormone levels return to normal, Patients who also take high amounts of any medication used to treat thyroid disorders.
How is Hyperthyroidism Diagnosed?
Hyperthyroidism is easily diagnosed once the disease is suspected, simple blood tests which measure thyroid stimulating hormones TSH which comes directly from your pituitary gland which it’s purpose is to tell your thyroid to produce thyroid hormone, and once your pituitary gland realizes that there is an excess in thyroid hormones it stops producing the TSH, When tested if your TSH blood level is low which clues your doctor into the fact that your thyroid if over producing hormone all by itself causing hyperthyroidism.
How is Hyperthyroidism treated?
In cases of heat palpations, tremors, and psychosis beta blocking medication can be given to get your central nervous system into check, the purpose of beta blocking medication is to stop the effects of the thyroid hormones with out effecting the thyroid gland, these types of medication do not cure hyperthyroidism they only stop the symptoms caused by the disease. If you have Graves disease anti- thyroid medications are prescribed, the idea here is to prevent the thyroid from producing thyroid hormones. When taken correctly anti-thyroid medication can get your hyperthyroidism under control in a very short time. When taking anti-thyroid medication routine blood work is ordered to check your livers function because your liver can become inflamed or a shortage of white blood cells signs of inflamed liver include yellowing of the skin and white of the eyes this is called jaundice, you may experience a high fever or a severely sore throat if any of these happen to you, stop taking your medication immediately then contact your doctor. Hyperthyroidism usually comes back once you stop your medication in such cases treatment that permanent stops the thyroid from producing high levels of thyroid hormones. The most widely used permanent treatment is radio active iodine treatment, being the only cells in the body which absorb iodine given in a radio active form damages or kills the thyroid cells off because the thyroid cells are the only cell in your body which can absorb iodine. The most common side effect from radioactive treatment is that it causes the thyroid to under produce thyroid hormones which in turn does the opposite causing hypothyroidism (under active thyroid) because radio active treatment kill to many thyroid cells. The only other treatment to permanently stop the thyroid from producing high levels of thyroid hormone is to have your thyroid surgically removed.
